掌握 Nuxt 3 中的状态管理:实践指南
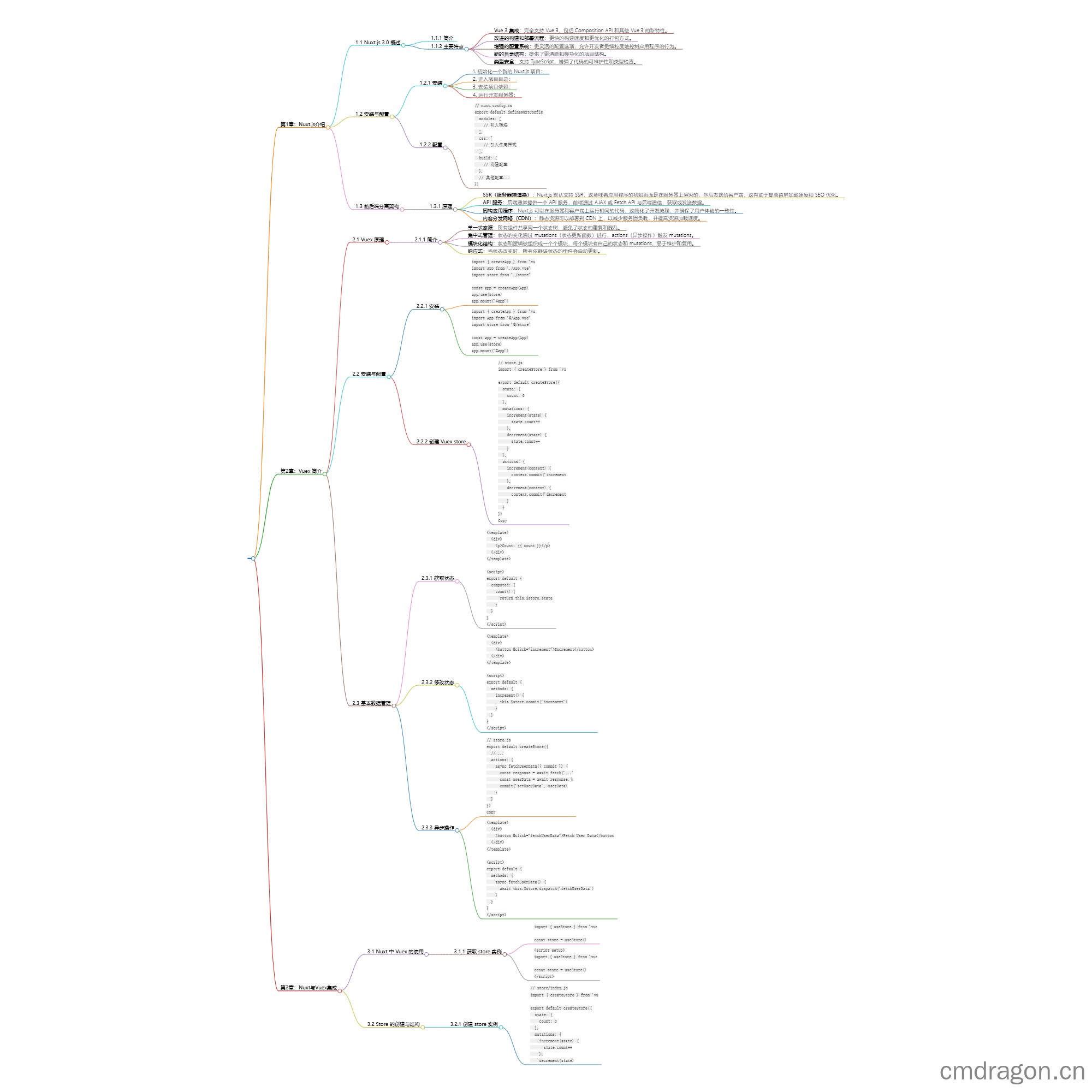

第1章:Nuxt 3 简介
1.1 Nuxt.js 3.0概述
Nuxt.js 是一个基于 Vue.js 的服务器端渲染(SSR)框架,它为开发者提供了一个优雅的架构,用于创建服务端渲染的Vue应用。Nuxt.js 3.0 是该框架的下一代版本,它建立在 Vue 3 的基础上,利用 Vue 3 的 Composition API 提供更强大的功能和更灵活的开发体验。
Nuxt 3.0 的主要特点包括:
- Vue 3 集成:完全支持 Vue 3,包括 Composition API 和其他 Vue 3 的新特性。
- 改进的构建和部署流程:更快的构建速度和更优化的打包方式。
- 增强的配置系统:更灵活的配置选项,允许开发者更细粒度地控制应用的行为。
- 新的目录结构:提供了更清晰和模块化的项目结构。
- 类型安全:支持 TypeScript,增强了代码的可维护性和类型检查。
1.2 安装与配置
在开始使用 Nuxt 3 之前,确保你的开发环境中已经安装了 Node.js(推荐版本为 LTS)。以下是在项目中安装 Nuxt 3 的步骤:
初始化一个新的 Nuxt 3 项目:
npx nuxi init my-nuxt3-project
进入项目目录:
cd my-nuxt3-project
安装项目依赖:
npm install
运行开发服务器:
npm run dev
默认情况下,Nuxt 3 会监听 http://localhost:3000 地址。
对于配置,Nuxt 3 提供了 nuxt.config.ts(或 .js)文件,你可以在这里定制应用的配置,例如:
// nuxt.config.ts
export default defineNuxtConfig({
modules: [
// 引入模块
],
css: [
// 引入全局样式
],
build: {
// 构建配置
},
// 其他配置...
})
1.3 前后端分离架构
Nuxt.js 作为一个SSR框架,天然支持前后端分离的架构。在这种架构中,前端负责用户界面和交互,而后端负责数据处理和业务逻辑。以下是前后端分离架构的几个关键点:
- SSR(服务器端渲染):Nuxt.js 默认支持SSR,这意味着应用的初始页面是在服务器上渲染的,然后发送给客户端,这有助于提高首屏加载速度和SEO优化。
- API服务:后端通常提供一个API服务,前端通过AJAX或Fetch API与后端通信,获取或发送数据。
- 同构应用:Nuxt.js 可以在服务器和客户端上运行相同的代码,这简化了开发流程,并确保了用户体验的一致性。
- 内容分发网络(CDN):静态资源可以部署到CDN上,以减少服务器负载,并提高资源加载速度。
通过使用 Nuxt.js 3,开发者可以更加便捷地构建符合现代Web应用要求的前后端分离架构。
第2章:Vuex简介
2.1 Vuex原理
Vuex 是一个专为 Vue.js 应用程序设计的状态管理模式,它提供了一种集中式存储应用状态的方式,使得状态能够以模块化和可预测的方式进行管理。Vuex 的核心原理是:
- 单一状态源:所有组件共享同一个状态树,避免了状态的重复和混乱。
- 集中式管理:状态的变化通过 mutations(状态更新函数)进行,actions(异步操作)触发 mutations。
- 模块化结构:状态和逻辑被组织成一个个模块,每个模块有自己的状态和 mutations,易于维护和复用。
- 响应式:当状态改变时,所有依赖该状态的组件会自动更新。
2.2 安装与配置
安装 Vuex 通常是在项目的 main.js 或 nuxt.config.js 中进行,如果你使用 Nuxt.js,可以在 nuxt.config.js 中添加:
1 | import { createApp } from 'vue' |
对于 Nuxt 3,你可以在 nuxt.config.ts 中导入并使用:
1 | import { createApp } from 'vue' |
2.3 基本数据管理
2.3.1 创建Vuex store
首先,创建一个名为 store.js 或 store.ts 的文件,定义你的状态(state)和动作(mutations):
1 | // store.js |
2.3.2 在组件中使用Vuex
在组件中,你可以通过 this.$store 访问 store,并通过 this.$store.dispatch 调用 actions:
1 | <template> |
通过以上步骤,你已经设置了基本的 Vuex 状态管理,所有的组件都可以通过 store 来共享和管理数据。
第3章:Nuxt 3与Vuex集成
3.1 Nuxt中Vuex的使用
在 Nuxt 3 中使用 Vuex 与在 Vue 中使用类似,只有一些细微差别。在 Nuxt 3 中,你可以在 composables 或 setup 函数中直接使用 useStore 函数来获取 store 实例。
首先,在你的项目中创建一个名为 store 的文件夹,并在其中创建一个名为 index.js 或 index.ts 的文件,用于存放你的 Vuex store。
3.2 Store的创建与结构
在 store/index.js 中创建一个 Vuex store 实例:
1 | // store/index.js |
3.3 mutations和actions
在 Nuxt 3 中,你可以在组件中使用 useStore 函数来获取 store 实例,并使用 mutations 和 actions:
1 | <template> |
在这个示例中,我们使用 useStore 函数获取了 store 实例,并使用 computed 函数获取了状态 count。当点击按钮时,调用 store.dispatch('increment') 来触发 increment action。
在 Nuxt 3 中,你可以使用 useStore 函数来获取 store 实例,并在组件中使用 mutations 和 actions。这种方式更加简单和直观,并且可以更好地与 Composition API 集成。
第4章:状态管理最佳实践
4.1 分模块管理
为了保持代码的可维护性和组织性,将 Vuex store 分模块管理是一个好习惯。创建多个小的 store 文件,每个文件专注于处理特定领域的数据。例如,你可以有 userStore.js、productStore.js 等。
1 | // userStore.js |
4.2 使用类型安全
使用 TypeScript 或 Flow 可以为 Vuex store 的状态、mutations 和 actions 提供类型安全。这有助于在编译时发现潜在的错误。
1 | // 使用TypeScript |
4.3 使用插件与中间件
- 插件:Vuex 提供了插件机制,可以用来共享通用的功能,如日志记录、状态检查等。例如,
vuex-router-sync可以自动同步路由变化到 store。 - 中间件:在 mutations 或 actions 中使用
context对象,可以添加全局的中间件,如在每次修改 state 时执行某些操作。
1 | // 添加全局中间件 |
4.4 子组件状态通信
子组件可以通过 store.dispatch 或 store.commit 与父组件或全局 store 通信。如果需要在子组件之间共享状态,可以考虑使用自定义事件或者 Vuex 的 mapState 和 mapActions。
1 | // 子组件 |
通过这些最佳实践,你可以更好地管理 Nuxt 3 中的状态,提高代码的可读性和可维护性。
第5章:Vuex 状态管理进阶
5.1 共享状态与隔离
在大型应用中,可能需要在多个模块间共享状态。首先,应该避免将多个模块中的状态合并为一个模块。相反,可以使用 mapState 或 mapGetters 在多个模块中访问同一状态。如果需要在模块之间共享状态,可以使用 Vuex 的 actions 或 modules 注册全局动作或模块。
1 | // store/index.js |
5.2 状态持久化(Local Storage、SSR)
为了在刷新页面后保持状态,可以使用 Local Storage 或 Cookie 来持久化状态。在服务端渲染 (SSR) 中,可以使用服务端状态来初始化客户端状态。
1 | // store/index.js |
5.3 状态的异步操作
在使用异步操作时,可以使用 Vuex 的 actions 和 promises 或 async/await 来处理。建议在 action 中处理异步操作,在 mutation 中处理同步操作。
1 | // store/index.js |
第6章:Vuex 3.x 新特性
Vuex 3.x 引入了一些新特性和改进,以更好地与 Vue 3 的 Composition API 集成。
6.1 Composition API 的使用
在 Vuex 3.x 中,为了与 Vue 3 的 Composition API 兼容,引入了 useStore 方法。这个方法允许你在组件中以 Composition API 的方式访问 Vuex store。
1 | <template> |
6.2 Refs 与 Computed 的结合
在 Composition API 中,你可以使用 ref 和 computed 来创建响应式引用和计算属性。结合 Vuex,你可以创建响应式的 store 属性和计算属性。
1 | <template> |
6.3 Proxy API 的优化
Vuex 3.x 利用 Vue 3 的 Proxy API 对 store 的状态进行了优化。这意味着状态的响应性现在是由 Vue 的响应性系统直接管理的,而不是 Vuex 内部实现。这使得 Vuex 的状态管理更加高效和可靠。
以下是一个示例,展示了如何使用 Vuex 3.x 中的 Proxy API:
1 | import { createStore } from 'vuex' |
在 Vuex 3.x 中,store.state 和 store.getters 都是响应式的,并且可以通过 Vue 的响应式系统进行访问和更新。这使得 Vuex 的状态管理更加符合 Vue 3 的设计理念,并且可以更紧密地与 Vue 3 的其他特性集成。
第7章:Vuex ORM 与 Nuxt
7.1 Vuex ORM 简介
Vuex ORM 是一个 Vuex 插件,提供了一种更简单、更可靠的方式来管理 Vuex 状态。它使用了类型化的数据模型和对象关系映射 (ORM) 概念,使得在 Vuex 中管理数据更加易于理解和维护。
7.2 数据模型与仓库
在 Vuex ORM 中,你可以创建数据模型,并将它们与 Vuex store 中的模块关联。数据模型是一个类,继承自 VuexORMAssert,并包含一些属性和方法。
以下是一个示例,展示了如何创建一个数据模型和关联到 Vuex store 中的模块:
1 | import { Model, VuexORMAssert } from 'vuex-orm' |
7.3 使用示例
在组件中,你可以使用 Vuex ORM 的数据模型和仓库来获取、更新和删除数据。
1 | <template> |
在这个示例中,我们使用了 Vuex ORM 的数据模型和仓库来获取用户数据,并在组件中显示它们。当点击 “Fetch Users” 按钮时,我们调用 fetchUsers 动作,从而获取用户数据并更新 Vuex store 中的状态。
在 Nuxt 中,你可以使用相同的方式来集成 Vuex ORM。只需要在 Nuxt 应用中安装 Vuex ORM 并在 Vuex 模块中创建数据模型和仓库,就可以在 Nuxt 组件中使用它们。
第8章:Redux 与 Nuxt 的对比
8.1 Redux 的介绍
Redux 是 JavaScript 状态容器,用于在应用中存储和管理状态。它遵循可预测性原则,并提供了一种单向数据流的架构,使得状态更易于理解和调试。Redux 通常与 React 和 React-Redux 一起使用,但也可以与其他库(如 Angular、Vue 等)结合使用。
8.2 何时选择 Redux
虽然 Vuex 在 Nuxt 中已经内置,并且在大多数情况下可以很好地满足需求,但有时候你可能需要使用 Redux 来管理状态。以下是一些情况:
- 跨多个组件共享状态:当你需要在多个组件之间共享状态时,Redux 可以提供更好的解决方案。
- 需要更复杂的状态管理:当你需要在多个组件之间同步状态,或者需要对状态进行更复杂的更新时,Redux 可以提供更好的支持。
- 需要更好的调试工具:Redux 提供了更好的调试工具,如 Redux DevTools,可以更好地追踪状态更新。
8.3 在 Nuxt 中引入 Redux 的策略
在 Nuxt 中引入 Redux 需要一些步骤:
- 安装依赖:首先,需要安装 Redux 和 React-Redux 依赖。
1 | yarn add redux react-redux |
- 创建 Redux store:在 Nuxt 应用中,可以在
plugins目录下创建一个redux.js文件,用于创建 Redux store。
1 | import { createStore } from 'redux' |
- 在 Nuxt 应用中使用 Redux store:在 Nuxt 应用中,可以使用
provide和inject函数,在应用的根组件中提供 Redux store,并在需要使用的组件中注入 store。
1 | <template> |
- 在组件中使用 Redux:在需要使用 Redux store 的组件中,可以使用
inject函数注入 store,并使用 React-Redux 的connect函数将 Redux store 连接到组件。
1 | <template> |
通过这些步骤,你可以在 Nuxt 应用中使用 Redux 来管理状态。
第9章:其他状态管理库
9.1 Nuxt 与 MobX
MobX 是一个轻量级的 JavaScript 状态管理库,它强调简洁和无侵入性,通过观察模式自动追踪对象的变化。在 Nuxt 中,MobX 可以与 Vue 2 或 Vue 3 结合使用,但相比 Vuex,它不需要显式地定义 store 和 action。
- 优点:轻量级,实时更新,易于理解和使用,对大型应用的性能影响较小。
- 缺点:对于复杂的大型应用,可能需要额外的工具来管理副作用和状态逻辑,不如 Vuex 那样结构化。
9.2 Nuxt 与 Pinia
Pinia 是 Vue 3 的官方状态管理模式,它是 Vuex 的轻量级替代品,旨在提供更简洁的 API。Pinia 与 Nuxt 结合时,可以使用 Vue 3 的特性,如 Composition API,使得状态管理更加直观。
- 优点:官方支持,与 Vue 3 无缝集成,易于理解和维护,没有复杂的中间件和生命周期。
- 缺点:对于 Nuxt 2,可能需要额外的适配,且对于需要复杂状态管理的场景,可能不如 Vuex 易于扩展。
9.3 选择状态管理库的考虑因素
- 应用大小和复杂性:对于小型应用或状态管理相对简单的场景,轻量级库如 MobX 或 Pinia 可能更合适。大型应用可能需要更强大的工具,如 Redux,来管理复杂的状态。
- 团队熟悉程度:团队成员是否熟悉某个库的使用方式,如果团队对某种库有深厚理解,选择它可能会提高开发效率。
- 性能:虽然现代库通常优化了性能,但对性能有严格要求的应用可能需要测量和对比不同库的性能。
- 可维护性和扩展性:长期来看,选择易于理解和维护的状态管理库是关键,特别是当应用需要扩展时。
- 社区支持和文档:活跃的社区和丰富的文档可以帮助解决遇到的问题,提高开发效率。
- 架构选择:如果你的项目使用了 Vue 3,那么 Pinia 可能是更好的选择,因为它是 Vue 生态的一部分。
第10章:实战项目
在Nuxt 3 中创建一个状态管理应用,我们可以使用 Vite 和 Vue 3 结合 TypeScript 和Vuex 4.x。以下是一个简化的步骤和代码结构概述:
初始化项目: 使用
npx create-nuxt-app my-app创建一个新的Nuxt 3 项目,然后安装Vuex:npm install vuex.创建Vuex store: 在
~/store目录下创建一个index.ts文件,作为Vuex store的入口:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30// store/index.ts
import { createStore } from 'vuex'
export default createStore({
state: () => ({
// 假设我们有用户信息和登录状态
user: null,
isLoggedIn: false,
}),
mutations: {
setUser(state, user) {
state.user = user
},
setIsLoggedIn(state, isLoggedIn) {
state.isLoggedIn = isLoggedIn
},
},
actions: {
// 异步操作
async login({ commit }, credentials) {
// ...登录逻辑
commit('setIsLoggedIn', true)
},
},
getters: {
// 计算属性
isLoggedIn: (state) => state.isLoggedIn,
},
})模块化(可选): 如果状态管理复杂,可以创建模块来组织。例如,创建
~/store/modules/auth.ts:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17// store/modules/auth.ts
import { defineStore } from 'vuex'
export const useAuthStore = defineStore('auth', {
state: () => ({
token: '',
}),
mutations: {
setToken(state, token) {
state.token = token
},
},
actions: {
// 登录相关操作
},
})在
index.ts中导入并使用:1
2
3
4
5import { useAuthStore } from '@/store/modules/auth'
// 在需要的地方导入并使用useAuthStore
const auth = useAuthStore()引入store到nuxt.config.ts: 在
nuxt.config.ts中,将store注册为全局插件:1
2
3
4
5
6import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import store from '@/store'
createApp(App).use(store).mount('#app')状态管理在组件中使用: 在组件中通过
$store访问状态和执行操作:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32<template>
<div>
{{ user.name }} ({{ isLoggedIn ? 'Logged in' : 'Logged out' }})
<button @click="login">Login</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { computed, onMounted, ref, store } from 'vue'
export default {
setup() {
const user = ref(null)
const isLoggedIn = computed(() => store.getters.isLoggedIn)
onMounted(() => {
// 初始化用户信息
store.dispatch('getUser')
})
const login = async () => {
await store.dispatch('login', { username: 'your_username' })
}
return {
user,
isLoggedIn,
login,
}
},
}
</script>面向服务端和客户端的优化:
- SSR(服务器端渲染) :Vuex在SSR中需要进行一些特殊处理,确保在服务端和客户端之间共享状态。可以使用
nuxtServerInit和storeOptions配置。 - CSP(内容安全策略) :确保在发送Vuex actions时使用
JSON.stringify序列化数据,避免跨站脚本攻击。 - 代码分割:如果应用很大,可以考虑使用
nuxt generate生成预加载的静态版本,减少首屏加载时间。
- SSR(服务器端渲染) :Vuex在SSR中需要进行一些特殊处理,确保在服务端和客户端之间共享状态。可以使用
这只是一个基本的框架,实际项目中可能还需要处理更多细节,比如错误处理、状态隔离等。记得在开发过程中遵循最佳实践和代码风格。
- Nuxt 3 路由系统详解:配置与实践指南 | cmdragon’s Blog
- Nuxt 3组件开发与管理 | cmdragon’s Blog
- Nuxt.js 深入浅出:目录结构与文件组织详解 | cmdragon’s Blog**
- 友情链接 | cmdragon’s Blog**
- 安装 Nuxt.js 的步骤和注意事项 | cmdragon’s Blog**
- 探索Web Components | cmdragon’s Blog**
- Vue微前端架构与Qiankun实践理论指南 | cmdragon’s Blog**
- Vue 3深度探索:自定义渲染器与服务端渲染 | cmdragon’s Blog**
- Tailwind CSS 响应式设计实战指南 | cmdragon’s Blog**
- Tailwind CSS 实战指南:快速构建响应式网页设计 | cmdragon’s Blog**
- Vue 3与ESLint、Prettier:构建规范化的前端开发环境 | cmdragon’s Blog**
- Vue TypeScript 实战:掌握静态类型编程 | cmdragon’s Blog**
