驾驭FastAPI多数据库:从读写分离到跨库事务的艺术

扫描二维码
关注或者微信搜一搜:编程智域 前端至全栈交流与成长
探索数千个预构建的 AI 应用,开启你的下一个伟大创意:https://tools.cmdragon.cn/
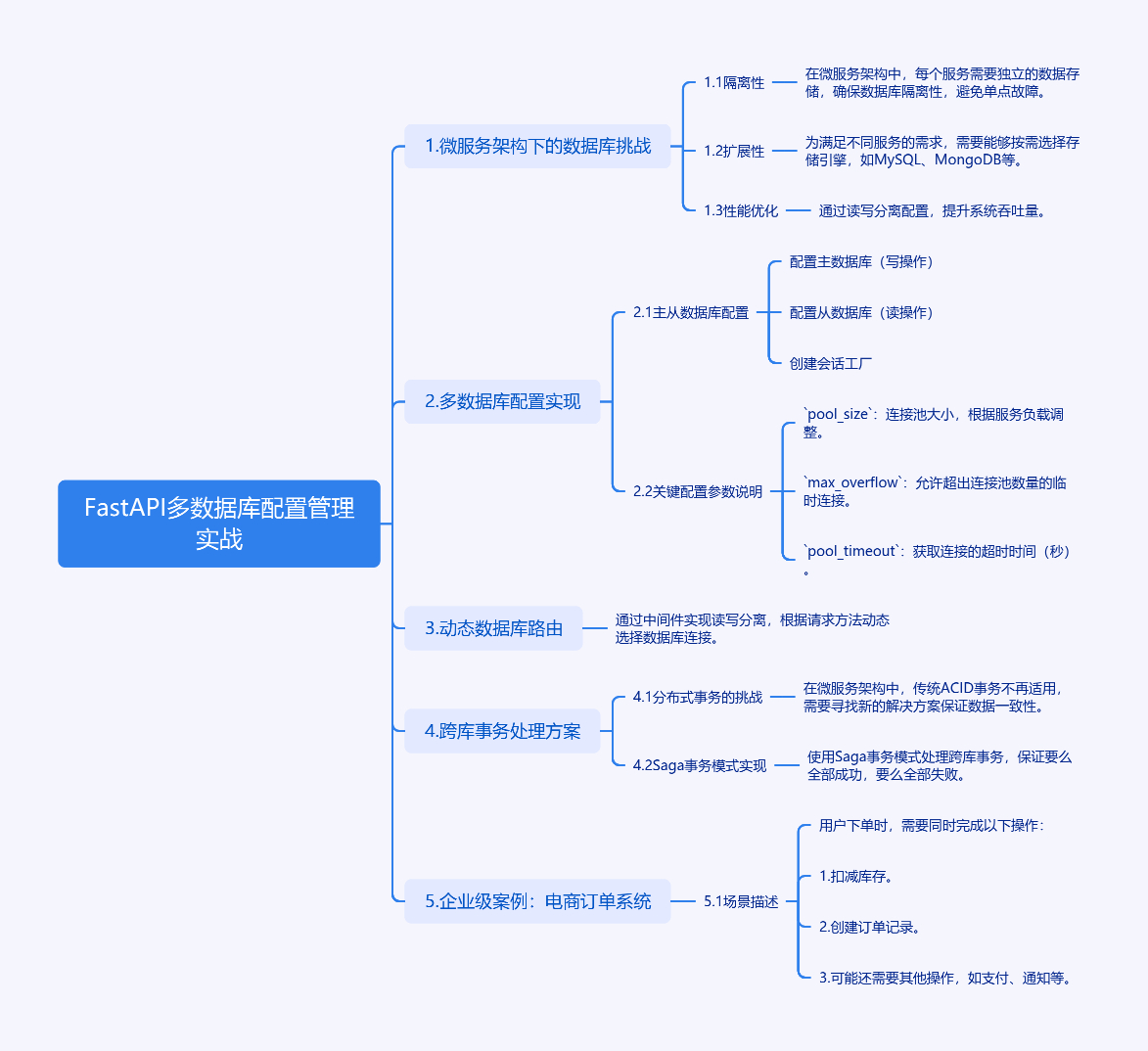
1. FastAPI多数据库配置管理实战
1.1 微服务架构下的数据库挑战
在微服务架构中,每个服务通常需要独立的数据存储。就像大型图书馆需要将不同学科的书籍分馆存放一样,电商系统可能将用户数据、订单数据、商品数据分别存储在不同数据库。这种架构带来三个核心需求:
- 隔离性:每个服务的数据库独立运行,避免单点故障
- 扩展性:不同数据库可按需选择存储引擎(如MySQL、MongoDB)
- 性能优化:读写分离配置可提升系统吞吐量
1.2 多数据库配置实现
以下示例展示如何在FastAPI中配置主从数据库:
1 | # database.py |
关键配置参数说明:
pool_size:连接池大小,根据服务负载调整max_overflow:允许超出连接池数量的临时连接pool_timeout:获取连接的超时时间(秒)
1.3 动态数据库路由
通过中间件实现读写分离:
1 | # dependencies.py |
2. 跨库事务处理方案
2.1 分布式事务的挑战
当订单服务需要同时更新订单库和扣减库存库时,传统ACID事务不再适用。这就像需要同时在两个不同银行账户之间转账,必须保证要么全部成功,要么全部失败。
2.2 Saga事务模式实现
1 | # services/transaction_coordinator.py |
3. 企业级案例:电商订单系统
3.1 场景描述
用户下单时需要同时操作:
- 订单数据库(PostgreSQL)
- 库存数据库(MongoDB)
- 用户积分数据库(MySQL)
3.2 完整实现代码
1 | # models.py |
课后Quiz
问题1: 当使用多个数据库时,如何保证跨库查询的事务一致性?
A. 使用数据库自带的分布式事务功能
B. 采用最终一致性模式配合补偿机制
C. 强制所有操作使用同个数据库
D. 增加重试机制自动处理失败
答案: B
解析: 在微服务架构中,不同服务通常使用不同数据库实例,传统ACID事务难以实施。采用Saga模式等最终一致性方案,配合补偿事务(如订单取消时的库存回补),是更可行的解决方案。
常见报错解决方案
错误1: MultipleResultsFound: Multiple rows were found when one was required
原因: 查询语句返回了多个结果,但期望单个结果
解决:
- 检查查询条件是否足够精确
- 使用
.first()代替.one() - 添加LIMIT 1子句
错误2: InterfaceError: Connection already closed
原因: 数据库连接过早关闭
预防:
- 使用上下文管理器管理会话
- 检查连接池配置
- 增加连接存活检测
1 | # 正确使用方式 |
错误3: DBAPIError: Can't reconnect until invalid transaction is rolled back
原因: 未正确处理事务回滚
解决:
- 在异常处理中添加显式回滚
- 设置事务自动回滚
1 | async def safe_transaction(): |
余下文章内容请点击跳转至 个人博客页面 或者 扫码关注或者微信搜一搜:编程智域 前端至全栈交流与成长,阅读完整的文章:
往期文章归档:
- 数据库事务隔离与Alembic数据恢复的实战艺术 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI与Alembic:数据库迁移的隐秘艺术 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 飞行中的引擎更换:生产环境数据库迁移的艺术与科学 | cmdragon’s Blog
- Alembic迁移脚本冲突的智能检测与优雅合并之道 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 多数据库迁移的艺术:Alembic在复杂环境中的精妙应用 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 数据库事务回滚:FastAPI中的存档与读档大法 | cmdragon’s Blog
- Alembic迁移脚本:让数据库变身时间旅行者 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 数据库连接池:从银行柜台到代码世界的奇妙旅程 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 点赞背后的技术大冒险:分布式事务与SAGA模式 | cmdragon’s Blog
- N+1查询:数据库性能的隐形杀手与终极拯救指南 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI与Tortoise-ORM开发的神奇之旅 | cmdragon’s Blog
- DDD分层设计与异步职责划分:让你的代码不再“异步”混乱 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 异步数据库事务锁:电商库存扣减的防超卖秘籍 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI中的复杂查询与原子更新指南 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 深入解析Tortoise-ORM关系型字段与异步查询 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI与Tortoise-ORM模型配置及aerich迁移工具 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 异步IO与Tortoise-ORM的数据库 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI数据库连接池配置与监控 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 分布式事务在点赞功能中的实现 | cmdragon’s Blog
- Tortoise-ORM级联查询与预加载性能优化 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 使用Tortoise-ORM和FastAPI构建评论系统 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 分层架构在博客评论功能中的应用与实现 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 深入解析事务基础与原子操作原理 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 掌握Tortoise-ORM高级异步查询技巧 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI与Tortoise-ORM实现关系型数据库关联 | cmdragon’s Blog
- Tortoise-ORM与FastAPI集成:异步模型定义与实践 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 异步编程与Tortoise-ORM框架 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI数据库集成与事务管理 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI与SQLAlchemy数据库集成 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI与SQLAlchemy数据库集成与CRUD操作 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI与SQLAlchemy同步数据库集成 | cmdragon’s Blog
- SQLAlchemy 核心概念与同步引擎配置详解 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI依赖注入性能优化策略 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI安全认证中的依赖组合 | cmdragon’s Blog
- XML Sitemap
