点赞背后的技术大冒险:分布式事务与SAGA模式

扫描二维码
关注或者微信搜一搜:编程智域 前端至全栈交流与成长
探索数千个预构建的 AI 应用,开启你的下一个伟大创意:https://tools.cmdragon.cn/
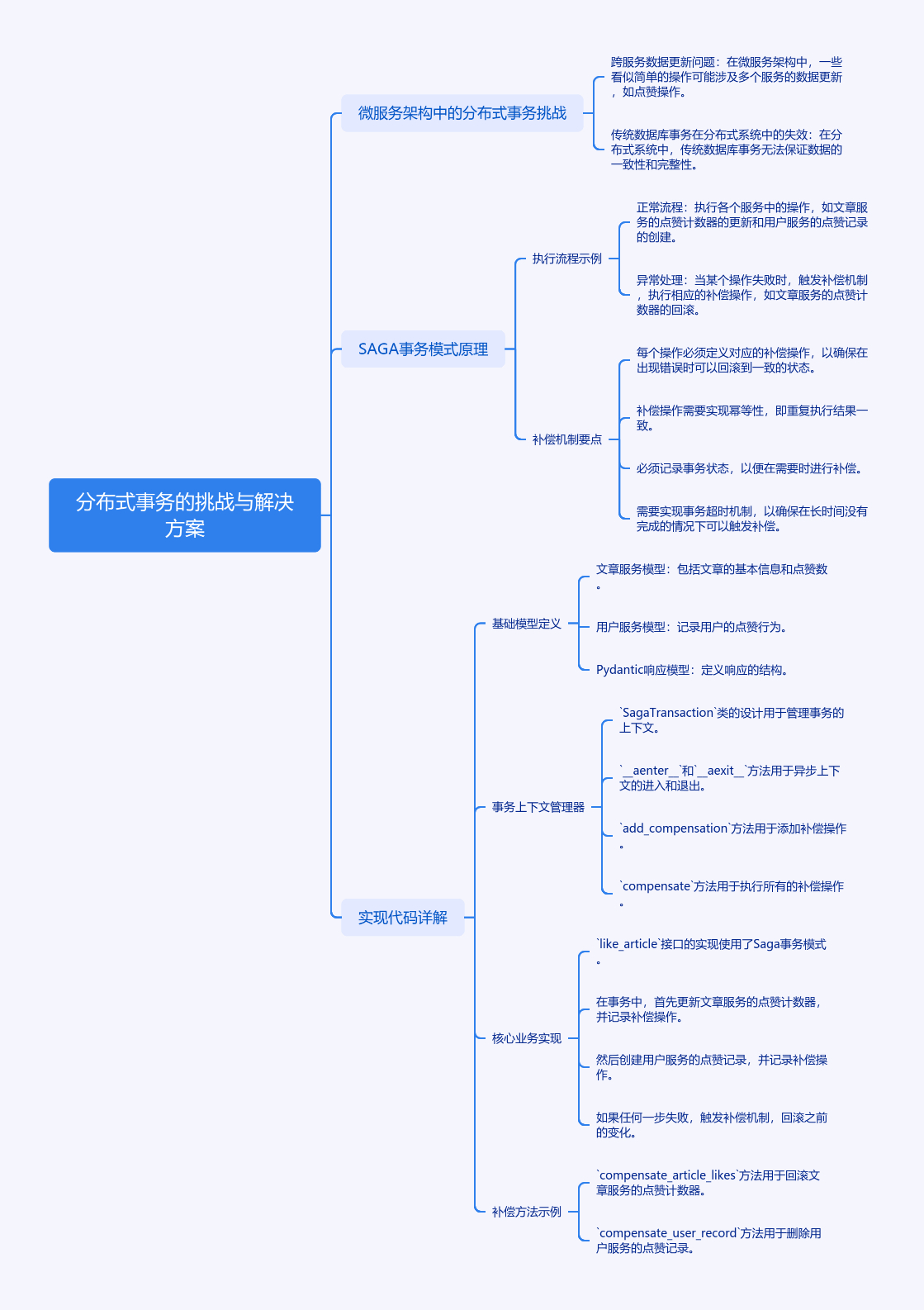
1. 分布式事务的挑战与解决方案
在微服务架构中,点赞这类看似简单的操作可能涉及多个服务的数据更新。假设我们有两个微服务:
- 文章服务(存储文章信息和点赞数)
- 用户服务(记录用户点赞行为)
当用户点赞时,需要同时更新:
- 文章服务的点赞计数器
- 用户服务的点赞记录
传统数据库事务在分布式系统中失效,我们需要采用SAGA事务模式。这种模式将事务分解为多个本地事务,通过补偿机制保证最终一致性。
2. SAGA事务模式原理
2.1 执行流程示例
正常流程:
1 | [文章服务+1] -> [用户服务创建记录] |
异常处理:
1 | [文章服务+1] -> [用户服务失败] -> [文章服务-1补偿] |
2.2 补偿机制要点
- 每个操作必须定义对应的补偿操作
- 补偿操作需要幂等(重复执行结果一致)
- 必须记录事务状态
- 需要实现事务超时机制
3. 实现代码详解
3.1 基础模型定义
1 | # 文章服务模型 |
3.2 事务上下文管理器
1 | class SagaTransaction: |
3.3 核心业务实现
1 |
|
4. 测试与验证
4.1 正常流程测试
1 | async def test_successful_like(): |
4.2 异常流程测试
1 | async def test_failed_transaction(): |
5. 课后Quiz
Q1:为什么补偿操作需要设计为幂等?
A. 提高系统性能
B. 防止重复补偿导致数据错误
C. 减少数据库连接数
D. 满足HTTP协议规范
正确答案:B
解析:网络重试可能导致补偿操作被多次触发,幂等设计确保多次执行结果一致,避免数据不一致。
Q2:以下哪些情况需要触发补偿机制?(多选)
A. 用户服务数据库连接超时
B. 文章不存在返回404错误
C. 用户重复点赞
D. 数据库主从同步延迟
正确答案:A
解析:404属于业务校验错误应在事务开始前检查,重复点赞属于业务逻辑错误,主从同步属于基础架构问题。只有跨服务操作失败需要补偿。
6. 常见报错与解决方案
报错1:TransactionManagementError - 事务已关闭
1 | TransactionManagementError: Transaction already closed |
原因:异步上下文管理器中过早关闭数据库连接
解决方案:
- 检查事务作用域范围
- 确保所有数据库操作在同一个事务上下文中
- 更新Tortoise-ORM到最新版本
报错2:HTTP 422 Unprocessable Entity
1 | { |
原因:请求体缺少必要字段或类型不匹配
解决方案:
- 检查请求头是否包含
X-User-ID - 验证URL参数类型是否正确
- 使用Swagger文档测试接口格式
报错3:TimeoutError - 数据库操作超时
1 | TimeoutError: Connection pool exhausted |
原因:数据库连接池不足或查询未优化
解决方案:
- 增加连接池大小配置:
1 | TORTOISE_CONFIG["connections"]["default"]["pool_size"] = 20 |
- 为高频查询字段添加索引
- 使用
select_related优化关联查询
7. 生产环境建议
- 添加事务日志:
1 | class TransactionLog(Tortoise.Model): |
- 实现定时补偿任务:
1 | async def check_hanging_transactions(): |
- 服务降级策略:
- 当连续补偿失败超过阈值时,触发人工干预警报
- 提供强制完成事务的管理员接口
- 实现事务状态查询接口供前端展示
(完整示例代码需配合PostgreSQL数据库运行,安装依赖:fastapi uvicorn tortoise-orm httpx python-multipart)
余下文章内容请点击跳转至 个人博客页面 或者 扫码关注或者微信搜一搜:编程智域 前端至全栈交流与成长,阅读完整的文章:
往期文章归档:
- N+1查询:数据库性能的隐形杀手与终极拯救指南 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI与Tortoise-ORM开发的神奇之旅 | cmdragon’s Blog
- DDD分层设计与异步职责划分:让你的代码不再“异步”混乱 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 异步数据库事务锁:电商库存扣减的防超卖秘籍 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI中的复杂查询与原子更新指南 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 深入解析Tortoise-ORM关系型字段与异步查询 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI与Tortoise-ORM模型配置及aerich迁移工具 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 异步IO与Tortoise-ORM的数据库 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI数据库连接池配置与监控 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 分布式事务在点赞功能中的实现 | cmdragon’s Blog
- Tortoise-ORM级联查询与预加载性能优化 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 使用Tortoise-ORM和FastAPI构建评论系统 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 分层架构在博客评论功能中的应用与实现 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 深入解析事务基础与原子操作原理 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 掌握Tortoise-ORM高级异步查询技巧 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI与Tortoise-ORM实现关系型数据库关联 | cmdragon’s Blog
- Tortoise-ORM与FastAPI集成:异步模型定义与实践 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 异步编程与Tortoise-ORM框架 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI数据库集成与事务管理 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI与SQLAlchemy数据库集成 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI与SQLAlchemy数据库集成与CRUD操作 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI与SQLAlchemy同步数据库集成 | cmdragon’s Blog
- SQLAlchemy 核心概念与同步引擎配置详解 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI依赖注入性能优化策略 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI安全认证中的依赖组合 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI依赖注入系统及调试技巧 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI依赖覆盖与测试环境模拟 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI中的依赖注入与数据库事务管理 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI依赖注入实践:工厂模式与实例复用的优化策略 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI依赖注入:链式调用与多级参数传递 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI依赖注入:从基础概念到应用 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI中实现动态条件必填字段的实践 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI中Pydantic异步分布式唯一性校验 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 掌握FastAPI与Pydantic的跨字段验证技巧 | cmdragon’s Blog
- XML Sitemap
