FastAPI安全异常处理:从401到422的奇妙冒险

扫描二维码
关注或者微信搜一搜:编程智域 前端至全栈交流与成长
探索数千个预构建的 AI 应用,开启你的下一个伟大创意:https://tools.cmdragon.cn/
第一章:FastAPI安全异常处理核心原理与实践
(注:根据用户要求,章节编号从”第一章”开始,不使用”深入”等词汇)
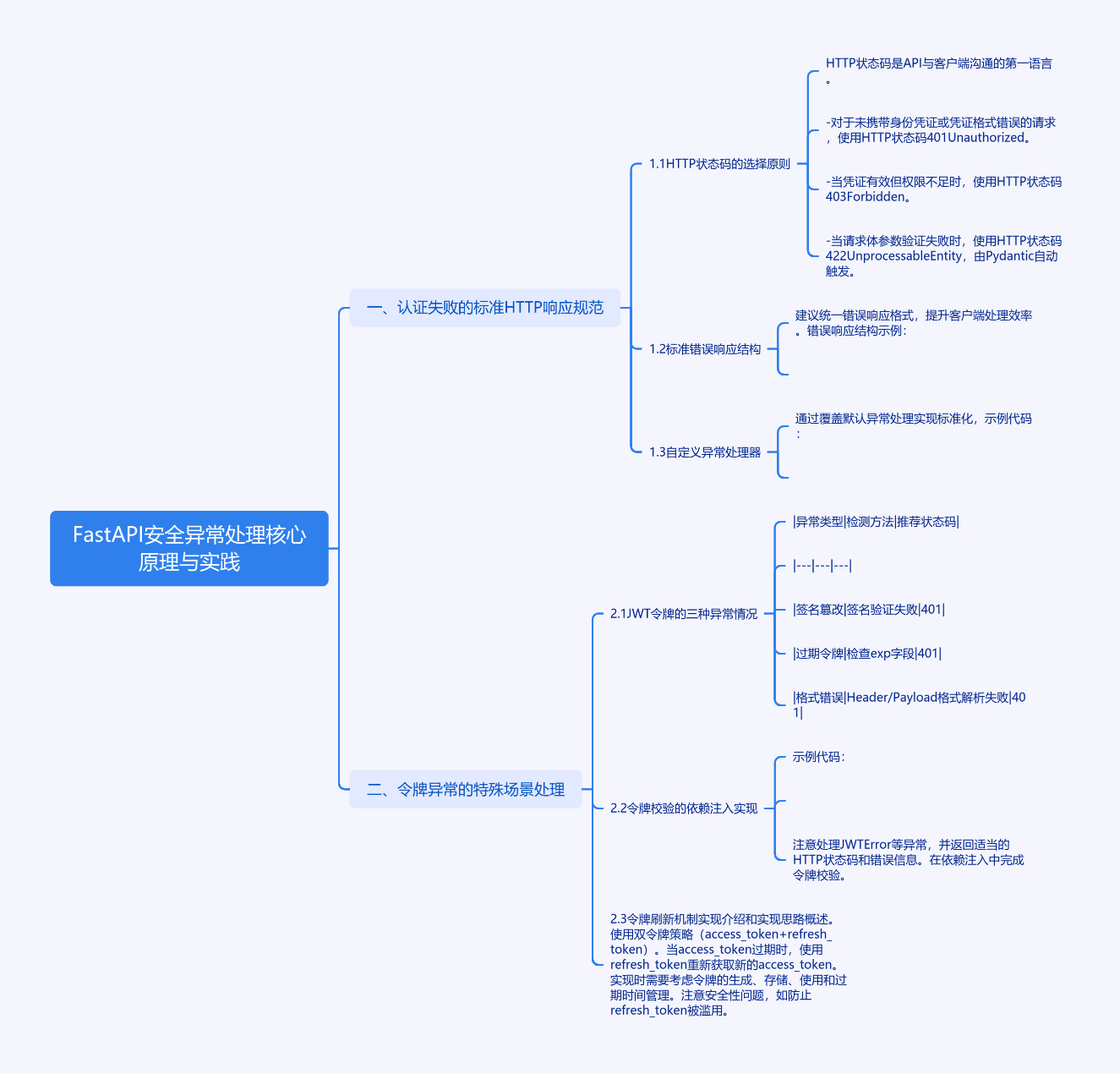
一、认证失败的标准HTTP响应规范
1.1 HTTP状态码的选择原则
HTTP状态码是API与客户端沟通的第一语言。FastAPI建议采用以下规范:
- 401 Unauthorized:当请求未携带身份凭证,或凭证格式错误时使用
- 403 Forbidden:当凭证有效但权限不足时使用
- 422 Unprocessable Entity:当请求体参数验证失败时使用(由Pydantic自动触发)
示例:访问需要管理员权限的接口时,普通用户会收到403而非401,因为此时凭证验证已通过,但权限不足
1.2 标准错误响应结构
建议统一错误响应格式以提升客户端处理效率:
1 | { |
1.3 自定义异常处理器
通过覆盖默认异常处理实现标准化:
1 | from fastapi import FastAPI, HTTPException, Request |
二、令牌异常的特殊场景处理
2.1 JWT令牌的三种异常情况
| 异常类型 | 检测方法 | 推荐状态码 |
|---|---|---|
| 签名篡改 | 签名验证失败 | 401 |
| 过期令牌 | 检查exp字段 | 401 |
| 格式错误 | Header/Payload格式解析失败 | 401 |
2.2 令牌校验的依赖注入实现
1 | from jose import JWTError, jwt |
2.3 令牌刷新机制实现
使用双令牌策略(access_token + refresh_token):
1 | from datetime import datetime, timedelta |
三、完整示例代码
1 | # requirements.txt |
课后Quiz
当JWT令牌的签名被篡改时,应该返回什么HTTP状态码?
A) 400
B) 401
C) 403
D) 500答案:B
解析:签名篡改属于凭证验证失败,应返回401 Unauthorized。403用于已认证用户权限不足的情况。如何判断JWT令牌是否过期?
A) 检查签发时间(iat)
B) 比较当前时间与exp字段
C) 验证签名有效性
D) 解析payload内容答案:B
解析:exp字段存储的是UTC时间戳,解码后与当前时间比较即可判断是否过期
常见报错解决方案
报错1:jose.exceptions.JWTDecodeError: Signature verification failed
原因:令牌签名与服务器密钥不匹配
解决步骤:
- 检查SECRET_KEY配置是否一致
- 验证请求头Authorization格式是否正确
- 确认令牌未经过篡改
报错2:HTTP 401 Unauthorized - Token expired
原因:访问时令牌已超过exp时间
解决方案:
- 引导用户重新登录获取新令牌
- 实现令牌刷新接口
- 前端应自动处理令牌刷新流程
预防建议:
- 令牌有效期不宜过长(建议access_token 15-30分钟)
- 使用https防止令牌泄露
- 服务端密钥应通过环境变量注入,禁止硬编码
(全文完)
余下文章内容请点击跳转至 个人博客页面 或者 扫码关注或者微信搜一搜:编程智域 前端至全栈交流与成长,阅读完整的文章:
往期文章归档:
- FastAPI权限迷宫:RBAC与多层级依赖的魔法通关秘籍 | cmdragon’s Blog
- JWT令牌:从身份证到代码防伪的奇妙之旅 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI安全认证:从密码到令牌的魔法之旅 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 密码哈希:Bcrypt的魔法与盐值的秘密 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 用户认证的魔法配方:从模型设计到密码安全的奇幻之旅 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI安全门神:OAuth2PasswordBearer的奇妙冒险 | cmdragon’s Blog
- OAuth2密码模式:信任的甜蜜陷阱与安全指南 | cmdragon’s Blog
- API安全大揭秘:认证与授权的双面舞会 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 异步日志监控:FastAPI与MongoDB的高效整合之道 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI与MongoDB分片集群:异步数据路由与聚合优化 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI与MongoDB Change Stream的实时数据交响曲 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 地理空间索引:解锁日志分析中的位置智慧 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 异步之舞:FastAPI与MongoDB的极致性能优化之旅 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 异步日志分析:MongoDB与FastAPI的高效存储揭秘 | cmdragon’s Blog
- MongoDB索引优化的艺术:从基础原理到性能调优实战 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 解锁FastAPI与MongoDB聚合管道的性能奥秘 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 异步之舞:Motor驱动与MongoDB的CRUD交响曲 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 异步之舞:FastAPI与MongoDB的深度协奏 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 数据库迁移的艺术:FastAPI生产环境中的灰度发布与回滚策略 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 数据库迁移的艺术:团队协作中的冲突预防与解决之道 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 驾驭FastAPI多数据库:从读写分离到跨库事务的艺术 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 数据库事务隔离与Alembic数据恢复的实战艺术 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI与Alembic:数据库迁移的隐秘艺术 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 飞行中的引擎更换:生产环境数据库迁移的艺术与科学 | cmdragon’s Blog
- Alembic迁移脚本冲突的智能检测与优雅合并之道 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 多数据库迁移的艺术:Alembic在复杂环境中的精妙应用 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 数据库事务回滚:FastAPI中的存档与读档大法 | cmdragon’s Blog
- Alembic迁移脚本:让数据库变身时间旅行者 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 数据库连接池:从银行柜台到代码世界的奇妙旅程 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 点赞背后的技术大冒险:分布式事务与SAGA模式 | cmdragon’s Blog
- N+1查询:数据库性能的隐形杀手与终极拯救指南 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI与Tortoise-ORM开发的神奇之旅 | cmdragon’s Blog
- DDD分层设计与异步职责划分:让你的代码不再“异步”混乱 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 异步数据库事务锁:电商库存扣减的防超卖秘籍 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI中的复杂查询与原子更新指南 | cmdragon’s Blog
- XML Sitemap
