FastAPI复杂查询终极指南:告别if-else的现代化过滤架构

扫描二维码关注或者微信搜一搜:编程智域 前端至全栈交流与成长
💣【传统架构的毁灭性缺陷】
- 致命缺陷1:硬编码字段导致每次新增条件需修改3个文件
- 致命缺陷2:排序参数与业务逻辑深度耦合
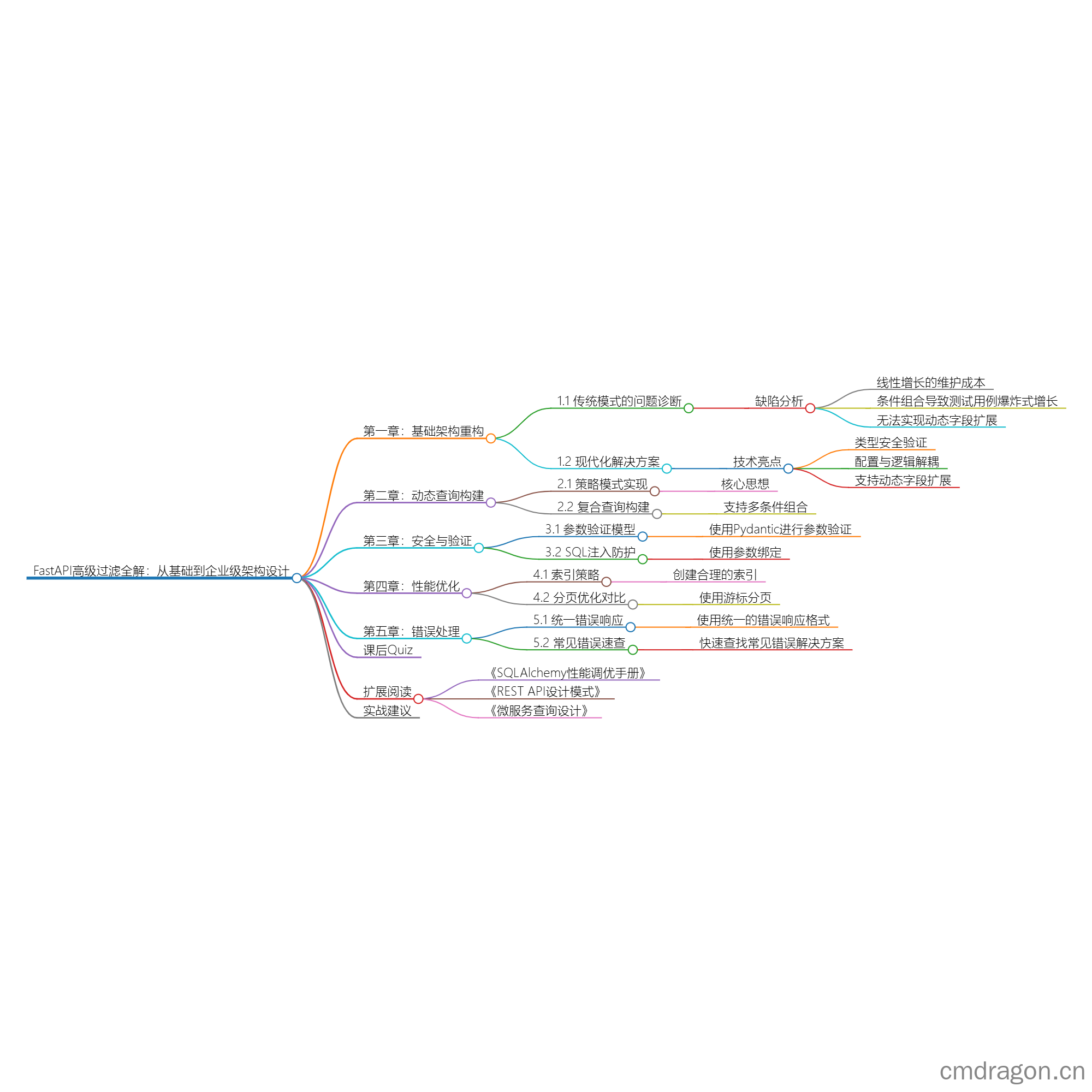
✨ 现代化解决方案架构图
1 | graph TD |
第一章:基础架构重构
1.1 传统模式的问题诊断
1 | # 典型问题代码 |
缺陷分析:
- 线性增长的维护成本(每新增条件需修改代码)
- 条件组合导致测试用例爆炸式增长
- 无法实现动态字段扩展
1.2 现代化解决方案
1 | # 声明式过滤配置 |
技术亮点:
- 类型安全验证(自动过滤非法类型参数)
- 配置与逻辑解耦(新增条件只需修改配置)
- 支持动态字段扩展
第二章:动态查询构建
2.1 策略模式实现
1 | class FilterStrategy: |
2.2 复合查询构建
1 | from sqlalchemy import and_, or_ |
第三章:安全与验证
3.1 参数验证模型
1 | from pydantic import BaseModel, conlist, confloat |
3.2 SQL注入防护
1 | # 不安全做法(绝对禁止!) |
第四章:性能优化
4.1 索引策略
1 | -- 复合索引 |
4.2 分页优化对比
1 | # 传统分页(性能随offset增大线性下降) |
第五章:错误处理
5.1 统一错误响应
1 |
|
5.2 常见错误速查
| 错误码 | 场景 | 解决方案 |
|---|---|---|
| 422 | 参数类型错误 | 检查Pydantic模型约束条件 |
| 500 | 无效排序字段 | 添加字段白名单验证 |
| 429 | 复杂查询频率过高 | 实现基于查询复杂度的限流策略 |
课后Quiz
Q1:如何安全处理用户输入的排序参数?
A) 直接拼接字符串到order_by
B) 使用字段白名单验证
C) 完全依赖前端验证
Q2:哪种分页方式更适合大数据量场景?
- Offset分页
- 游标分页
- 随机分页
Q3:如何验证价格区间的有效性?
- 在前端进行验证
- 使用Pydantic自定义校验器
- 在数据库添加CHECK约束
扩展阅读
- 《SQLAlchemy性能调优手册》 - 深度解析查询优化技巧
- 《REST API设计模式》 - 过滤参数的标准实现规范
- 《微服务查询设计》 - 分布式环境下的过滤方案
余下文章内容请点击跳转至 个人博客页面 或者 扫码关注或者微信搜一搜:编程智域 前端至全栈交流与成长,阅读完整的文章:
往期文章归档:
- FastAPI 核心机制:分页参数的实现与最佳实践 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI 错误处理与自定义错误消息完全指南:构建健壮的 API 应用 🛠️ | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI 自定义参数验证器完全指南:从基础到高级实战 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI 参数别名与自动文档生成完全指南:从基础到高级实战 🚀 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI Cookie 和 Header 参数完全指南:从基础到高级实战 🚀 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI 表单参数与文件上传完全指南:从基础到高级实战 🚀 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI 请求体参数与 Pydantic 模型完全指南:从基础到嵌套模型实战 🚀 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI 查询参数完全指南:从基础到高级用法 🚀 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI 路径参数完全指南:从基础到高级校验实战 🚀 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI路由专家课:微服务架构下的路由艺术与工程实践 🌐 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI路由与请求处理进阶指南:解锁企业级API开发黑科技 🔥 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI路由与请求处理全解:手把手打造用户管理系统 🔌 | cmdragon’s Blog
- FastAPI极速入门:15分钟搭建你的首个智能API(附自动文档生成)🚀 | cmdragon’s Blog
- HTTP协议与RESTful API实战手册(终章):构建企业级API的九大秘籍 🔐 | cmdragon’s Blog
- HTTP协议与RESTful API实战手册(二):用披萨店故事说透API设计奥秘 🍕 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 从零构建你的第一个RESTful API:HTTP协议与API设计超图解指南 🌐 | cmdragon’s Blog
- Python异步编程进阶指南:破解高并发系统的七重封印 | cmdragon’s Blog
- Python异步编程终极指南:用协程与事件循环重构你的高并发系统 | cmdragon’s Blog
- Python类型提示完全指南:用类型安全重构你的代码,提升10倍开发效率 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 三大平台云数据库生态服务对决 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 分布式数据库解析 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 深入解析NoSQL数据库:从文档存储到图数据库的全场景实践 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 数据库审计与智能监控:从日志分析到异常检测 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 数据库加密全解析:从传输到存储的安全实践 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 数据库安全实战:访问控制与行级权限管理 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 数据库扩展之道:分区、分片与大表优化实战 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 查询优化:提升数据库性能的实用技巧 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 性能优化与调优:全面解析数据库索引 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 存储过程与触发器:提高数据库性能与安全性的利器 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 数据操作与事务:确保数据一致性的关键 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 深入掌握 SQL 深度应用:复杂查询的艺术与技巧 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 彻底理解数据库设计原则:生命周期、约束与反范式的应用 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 深入剖析实体-关系模型(ER 图):理论与实践全解析 | cmdragon’s Blog
- 数据库范式详解:从第一范式到第五范式 | cmdragon’s Blog
- PostgreSQL:数据库迁移与版本控制 | cmdragon’s Blog
